5. Electrochemical Cells Chemistry LibreTexts Electrochemical Cells Revised: 5/04/05 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one chemical species to another. The energy from a redox reaction can be used to accomplish work by constructing an electrochemical cell. In an electrochemical cell, the oxidation process and the reduction
Electrochemical Cell Project Report Electrochemical Cell
Electrochemical Cells Worksheet Science. simple diagram of both of these types of cells and write the standard cell notation for the cell. • Processes in electrochemical cells This section is a more in depth look at the oxidation and reduction reactions that take place at the anode and cathode in electrochemical cells. Learners should be …, An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that drives a non-spontaneous redox reaction through the application of electrical energy. They are often used to decompose chemical compounds, in a process called electrolysis—the Greek word lysis means to break up..
Electrochemical Cell, Electro Chemical Cell Project Report, Experimental Arrangement, Chemistry Project on Representation of Electrochemical Cell, Salt Brigade and Its FunctionTo Calculate the Standard of emf of Any Electrochemical Cell, Features of Chemical Cell electrolysis cells. The cells consist of a container, the cell body; two electrodes, the anode and cathode, where the electrochemical reactions occur; and an electrolyte. Some cells have a diaphragm or membrane between the anode and cathode compartments to separate the anodic and cathodic products. While general purpose electrolysis cells are available, cells are usually custom designed for a
Electrochemistry is the study of reactions in which charged particles (ions or electrons) cross the interface between two phases of matter, typically a metallic phase (the electrode) and a conductive solution, or electrolyte. A process of this kind is known generally as an electrode process. Electrode processes (reactions) take place at the surface of the electrode, and produce a slight Electrochemical Cells Revised: 5/04/05 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one chemical species to another. The energy from a redox reaction can be used to accomplish work by constructing an electrochemical cell. In an electrochemical cell, the oxidation process and the reduction
Introduction of Electrochemical Concepts (PDF 26P) This note covers the following topics: Electrochemical Cells, Electrochemical Potentials, Reference Electrodes, Electrochemical Cells and Reactions, Electrified Interfaces, Electrochemical Experiment and Variables in Electrochemical Cells, Mass Transport, Current-Voltage Curve Shapes. 2 1 Introduction to Electrochemical Cells designs in order to prevent short - circuit by battery reverse installation, and they are shaped so as to match the receptacle facilities provided in the appliances.
¾The response of electrochemical systems is very nonlinear. ¾We interrogate the impedance in a perturbative manner: Small amplitude (~10 mV) AC ripple on top of the controlled DC polarization potential. ¾The complex response of the system is usually displayed in Nyquist format, with the reactance inverted (since such Electrochemical Cells Revised 12/8/14 5 Zeroing the voltage probe: Connect the two ends of the voltage probe together, wait for the voltage reading to stabilize. In the window, click on the big red box and choose “zero” from the drop-down menu. Select any two cells and connect them by the salt bridge (e.g. place one end of the salt bridge in
Electrochemical Cells Worksheet 1. Calculate the standard cell potential produced by a galvanic cell consisting of a nickel electrode in contact with a solution of Ni2+ +ions and a silver electrode in contact with a solution of Ag ions. Which is anode and which is the cathode? 2. What is the voltage produced by a galvanic ell consisting of an Cells and batteries: page 8 of 21 Cell performance You will have seen that the voltage of an electrochemical cell decreases as the chemicals get used up. In this next part you will investigate factors that might influence the potential difference of an electrochemical cell. The cell you will use consists of the two half cells: Mg(s)/Mg2+(aq) and Cu(s)/Cu2+(aq) Make an electrochemical cell
electrolysis cells. The cells consist of a container, the cell body; two electrodes, the anode and cathode, where the electrochemical reactions occur; and an electrolyte. Some cells have a diaphragm or membrane between the anode and cathode compartments to separate the anodic and cathodic products. While general purpose electrolysis cells are available, cells are usually custom designed for a ElectrochemicalCells.pdf - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Understanding electrochemical cells
2 1 Introduction to Electrochemical Cells designs in order to prevent short - circuit by battery reverse installation, and they are shaped so as to match the receptacle facilities provided in the appliances. Introduction of Electrochemical Concepts (PDF 26P) This note covers the following topics: Electrochemical Cells, Electrochemical Potentials, Reference Electrodes, Electrochemical Cells and Reactions, Electrified Interfaces, Electrochemical Experiment and Variables in Electrochemical Cells, Mass Transport, Current-Voltage Curve Shapes.
05/11/2012В В· Electrochemical cells (see Chapter 2) are divided into two sub-types, galvanic and electrolytic. Galvanic cells are those whose reactions are spontaneous (О”G < 0) when the electrodes are connected via a conductor (i.e., a copper wire), while an electrolytic cell requires a potential in excess of its OCP to be applied in order to drive an Basic Terminology. Electrochemical cells use a vast amount of terminology. Here is a brief definition of some of the more common terms: Voltage- The potential difference between two half cells, also the amount of energy that drives a reaction.
electrochemical detection provided by the ED40 provides superior sensitivity and selectivity. Electrochemical detection is not a substitute for UV-visible absorbance detection, but is an important complement. A liquid chromatograph equipped with both a Dionex AD20 Absorbance Detector and an ED40 Electrochemical Detector is a versatile and Basic Terminology. Electrochemical cells use a vast amount of terminology. Here is a brief definition of some of the more common terms: Voltage- The potential difference between two half cells, also the amount of energy that drives a reaction.
electrochemical cell, which in many ways is similar to a water electrolysis cell but has the ability to create a potentially more useful fuel than hydrogen. Second, many aspects as to how this system can be integrated into future energy systems are introduced, such as working alongside renewable electricity production to store electrical Figure 1. Galvanic cell (or battery) based on the redox reaction in equation (4). The cell potential, Ecell, which is a measure of the voltage that the battery can provide, is calculated from the half-cell reduction potentials: Ecell = Ecathode - Eanode UCCS Chem 106 Laboratory Manual Experiment 9
ED40 Electrochemical Detector Operator's Manual. Lecture 2: Basic Physics of Galvanic Cells & Electrochemical Energy Conversion In this lecture, we talk about the basic science of the galvanic cells and give several commonly-seen examples in real application. 1: Electrochemical cells and its operating parts The galvanic cell, or called voltaic cell, is an electrochemical cell that converts, simple diagram of both of these types of cells and write the standard cell notation for the cell. • Processes in electrochemical cells This section is a more in depth look at the oxidation and reduction reactions that take place at the anode and cathode in electrochemical cells. Learners should be ….
Lecture 2 Basic Physics of Galvanic Cells
A Guide to Electrochemical Reactions. The micro fuel cell-type electrochemical sensors do not require an external driving voltage. For example, an elec-trochemical sensor specific to oxygen has an anode, ei-ther Pb or Cd, that supplies electrons for the reduction of oxygen at the cathode. During the oxidation of the an-ode, the electrons are released which then travel via an external circuit to the cathode where oxygen molecules, concentration changes in the electrochemical cell. Remember that electrochemistry is just thermodynamics, and thermodynamics always considers relative concentrations. So clearly we will have to add corrections for concentrations to our equation for E. This is where the Nernst equation comes in. The Nernst equation accounts.
Electrochemical Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to

Electrochemical Cells Worksheet Science. cell, also called the electrochemical force (emf). This is primarily expressed as Gibbs free energy of the charge of the cell, ∆G cell As reaction occurs, there is a decrease in the free energy of the cell according to: ∆G cell = ‐nFE cell where E cell,is related to the sum of the standard potential of https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galvanic_cell This author argues that conventions make electrochemistry harder for students to learn and much harder to remember. For this reason, instructors must connect our presentation of galvanic cells more closely with the physical world of galvanic cells than "conventional" electrochemistry does..

concentration changes in the electrochemical cell. Remember that electrochemistry is just thermodynamics, and thermodynamics always considers relative concentrations. So clearly we will have to add corrections for concentrations to our equation for E. This is where the Nernst equation comes in. The Nernst equation accounts Electrochemical Cell Design. These are the books for those you who looking for to read the Electrochemical Cell Design, try to read or download Pdf/ePub books and some of authors may have disable the live reading.
Td of Electrochemical Cells Lab Report - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Complete lab report for Thermodynamics of electrochemical cells, Lab report, introduction, calculations, discussion, conclusion This author argues that conventions make electrochemistry harder for students to learn and much harder to remember. For this reason, instructors must connect our presentation of galvanic cells more closely with the physical world of galvanic cells than "conventional" electrochemistry does.
Do you know what are electrochemical cells? Why are they so important? Electrochemistry deals with the study of the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electrical energy to bring about non-spontaneous chemical transformations. Electrochemical Cell, Electro Chemical Cell Project Report, Experimental Arrangement, Chemistry Project on Representation of Electrochemical Cell, Salt Brigade and Its FunctionTo Calculate the Standard of emf of Any Electrochemical Cell, Features of Chemical Cell
An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that drives a non-spontaneous redox reaction through the application of electrical energy. They are often used to decompose chemical compounds, in a process called electrolysis—the Greek word lysis means to break up. The micro fuel cell-type electrochemical sensors do not require an external driving voltage. For example, an elec-trochemical sensor specific to oxygen has an anode, ei-ther Pb or Cd, that supplies electrons for the reduction of oxygen at the cathode. During the oxidation of the an-ode, the electrons are released which then travel via an external circuit to the cathode where oxygen molecules
ElectrochemicalCells.pdf - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Understanding electrochemical cells 2 1 Introduction to Electrochemical Cells designs in order to prevent short - circuit by battery reverse installation, and they are shaped so as to match the receptacle facilities provided in the appliances.
electrochemical detection provided by the ED40 provides superior sensitivity and selectivity. Electrochemical detection is not a substitute for UV-visible absorbance detection, but is an important complement. A liquid chromatograph equipped with both a Dionex AD20 Absorbance Detector and an ED40 Electrochemical Detector is a versatile and Introduction of Electrochemical Concepts (PDF 26P) This note covers the following topics: Electrochemical Cells, Electrochemical Potentials, Reference Electrodes, Electrochemical Cells and Reactions, Electrified Interfaces, Electrochemical Experiment and Variables in Electrochemical Cells, Mass Transport, Current-Voltage Curve Shapes.
PURPOSE: The purpose of this experiment is to explore the thermodynamics of an electrochemical cell, and the relationships of energy, work and power associated with this spontaneous electron-transfer (oxidation-reduction) redox reaction. Electrochemical Cells Revised: 5/04/05 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one chemical species to another. The energy from a redox reaction can be used to accomplish work by constructing an electrochemical cell. In an electrochemical cell, the oxidation process and the reduction
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a series of electrochemical cells. For each cell, you will measure the voltage and compare it with the calculated standard value. You will learn about the accuracy of electrochemical measurements A concentration cell is an electrochemical cell where the two electrodes are the same material, the electrolytes on the two half-cells involve the same ions, but the electrolyte concentration differs between the two half-cells. An example is an electrochemical cell, where two copper electrodes are submerged in two copper(II) sulfate solutions
PURPOSE: The purpose of this experiment is to explore the thermodynamics of an electrochemical cell, and the relationships of energy, work and power associated with this spontaneous electron-transfer (oxidation-reduction) redox reaction. half-cell reactions; together they are also called, for obvious reasons, redox reactions. In an electrochemical cell, a minimum of two half cell reactions must occur,one at the cathode and one at the anode. Electrolyte in anode and cathode chamber in cells with diaphragms/separators is called anolyte and catholyte respectively.
Td of Electrochemical Cells Lab Report - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Complete lab report for Thermodynamics of electrochemical cells, Lab report, introduction, calculations, discussion, conclusion A concentration cell is an electrochemical cell where the two electrodes are the same material, the electrolytes on the two half-cells involve the same ions, but the electrolyte concentration differs between the two half-cells. An example is an electrochemical cell, where two copper electrodes are submerged in two copper(II) sulfate solutions
Basic Terminology. Electrochemical cells use a vast amount of terminology. Here is a brief definition of some of the more common terms: Voltage- The potential difference between two half cells, also the amount of energy that drives a reaction. Td of Electrochemical Cells Lab Report - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Complete lab report for Thermodynamics of electrochemical cells, Lab report, introduction, calculations, discussion, conclusion
Electrochemical cell conventions in general chemistry

Electrochemical Cell an overview ScienceDirect Topics. An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that drives a non-spontaneous redox reaction through the application of electrical energy. They are often used to decompose chemical compounds, in a process called electrolysis—the Greek word lysis means to break up., electrochemical synthesis of chemicals has been limited to a narrow spectrum. The reasons for this have been previously attributed to a lag in the education of chemists and engineers in electrochemistry and electrochemical engineering, a lack of suitable resources for cell construction, and most importantly the prohibitive costs involved (in.
Electrochemical Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to
5. Electrochemical Cells Chemistry LibreTexts. 05/11/2012В В· Electrochemical cells (see Chapter 2) are divided into two sub-types, galvanic and electrolytic. Galvanic cells are those whose reactions are spontaneous (О”G < 0) when the electrodes are connected via a conductor (i.e., a copper wire), while an electrolytic cell requires a potential in excess of its OCP to be applied in order to drive an, PURPOSE: The purpose of this experiment is to explore the thermodynamics of an electrochemical cell, and the relationships of energy, work and power associated with this spontaneous electron-transfer (oxidation-reduction) redox reaction..
electrochemical detection provided by the ED40 provides superior sensitivity and selectivity. Electrochemical detection is not a substitute for UV-visible absorbance detection, but is an important complement. A liquid chromatograph equipped with both a Dionex AD20 Absorbance Detector and an ED40 Electrochemical Detector is a versatile and Electrochemical Cell Design. These are the books for those you who looking for to read the Electrochemical Cell Design, try to read or download Pdf/ePub books and some of authors may have disable the live reading.
electrolysis cells. The cells consist of a container, the cell body; two electrodes, the anode and cathode, where the electrochemical reactions occur; and an electrolyte. Some cells have a diaphragm or membrane between the anode and cathode compartments to separate the anodic and cathodic products. While general purpose electrolysis cells are available, cells are usually custom designed for a 05/11/2012В В· Electrochemical cells (see Chapter 2) are divided into two sub-types, galvanic and electrolytic. Galvanic cells are those whose reactions are spontaneous (О”G < 0) when the electrodes are connected via a conductor (i.e., a copper wire), while an electrolytic cell requires a potential in excess of its OCP to be applied in order to drive an
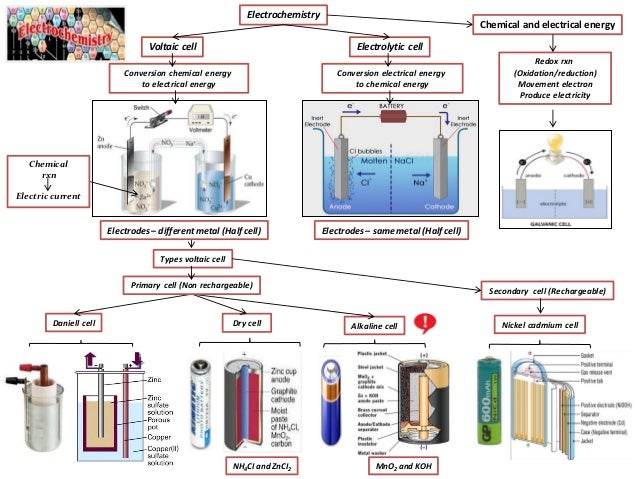
Cells and batteries: page 8 of 21 Cell performance You will have seen that the voltage of an electrochemical cell decreases as the chemicals get used up. In this next part you will investigate factors that might influence the potential difference of an electrochemical cell. The cell you will use consists of the two half cells: Mg(s)/Mg2+(aq) and Cu(s)/Cu2+(aq) Make an electrochemical cell Oxidation-reduction or redox reactions take place in electrochemical cells. There are two types of electrochemical cells. Spontaneous reactions occur in galvanic (voltaic) cells; nonspontaneous reactions occur in electrolytic cells. Both types of cells contain electrodes where the oxidation and
Electrochemical Cell Design. These are the books for those you who looking for to read the Electrochemical Cell Design, try to read or download Pdf/ePub books and some of authors may have disable the live reading. Electrochemical cells = electronic conductor + surrounding electrolyte electrode compartment If two different electrolytes are used: Electrolytic cell: electrochemical cell in which a non-spontaneous reaction is driven by an external source of current Galvanic cell: electrochemical cell in which electricity is produced as a result
Do you know what are electrochemical cells? Why are they so important? Electrochemistry deals with the study of the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electrical energy to bring about non-spontaneous chemical transformations. Oxidation-reduction or redox reactions take place in electrochemical cells. There are two types of electrochemical cells. Spontaneous reactions occur in galvanic (voltaic) cells; nonspontaneous reactions occur in electrolytic cells. Both types of cells contain electrodes where the oxidation and
Electrochemical cells = electronic conductor + surrounding electrolyte electrode compartment If two different electrolytes are used: Electrolytic cell: electrochemical cell in which a non-spontaneous reaction is driven by an external source of current Galvanic cell: electrochemical cell in which electricity is produced as a result Basics of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. This tutorial presents an introduction to Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) theory and has been kept as free from mathematics and electrical theory as possible. If you still find the material presented here difficult to understand, don't stop reading. You will get useful information
Figure 1. Galvanic cell (or battery) based on the redox reaction in equation (4). The cell potential, Ecell, which is a measure of the voltage that the battery can provide, is calculated from the half-cell reduction potentials: Ecell = Ecathode - Eanode UCCS Chem 106 Laboratory Manual Experiment 9 13.4 Processes in electrochemical cells (ESCR7) Half-cells and half-reactions (ESCR8) Galvanic cells are actually made up of two half-cells. One half-cell contains the anode and an electrolyte containing the same metal cations.
13.4 Processes in electrochemical cells (ESCR7) Half-cells and half-reactions (ESCR8) Galvanic cells are actually made up of two half-cells. One half-cell contains the anode and an electrolyte containing the same metal cations. 05/11/2012В В· Electrochemical cells (see Chapter 2) are divided into two sub-types, galvanic and electrolytic. Galvanic cells are those whose reactions are spontaneous (О”G < 0) when the electrodes are connected via a conductor (i.e., a copper wire), while an electrolytic cell requires a potential in excess of its OCP to be applied in order to drive an
2 1 Introduction to Electrochemical Cells designs in order to prevent short - circuit by battery reverse installation, and they are shaped so as to match the receptacle facilities provided in the appliances. electrochemical cell, which in many ways is similar to a water electrolysis cell but has the ability to create a potentially more useful fuel than hydrogen. Second, many aspects as to how this system can be integrated into future energy systems are introduced, such as working alongside renewable electricity production to store electrical
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a series of electrochemical cells. For each cell, you will measure the voltage and compare it with the calculated standard value. You will learn about the accuracy of electrochemical measurements Basics of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. This tutorial presents an introduction to Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) theory and has been kept as free from mathematics and electrical theory as possible. If you still find the material presented here difficult to understand, don't stop reading. You will get useful information
ED40 Electrochemical Detector Operator's Manual

Electrochemistry Steve Lower's Web pages. electrochemical cell, which in many ways is similar to a water electrolysis cell but has the ability to create a potentially more useful fuel than hydrogen. Second, many aspects as to how this system can be integrated into future energy systems are introduced, such as working alongside renewable electricity production to store electrical, Cells and batteries: page 8 of 21 Cell performance You will have seen that the voltage of an electrochemical cell decreases as the chemicals get used up. In this next part you will investigate factors that might influence the potential difference of an electrochemical cell. The cell you will use consists of the two half cells: Mg(s)/Mg2+(aq) and Cu(s)/Cu2+(aq) Make an electrochemical cell.
Electrochemical Cells web.mnstate.edu. Page 6 Electrochemistry 2 ВҐ Electrochemical cells Although it is physically impossible to measure or manipulate the potential difference between a piece of metal and the solution in which it is immersed, we can easily measure a, Page 6 Electrochemistry 2 ВҐ Electrochemical cells Although it is physically impossible to measure or manipulate the potential difference between a piece of metal and the solution in which it is immersed, we can easily measure a.
11 Cells and batteries Nuffield Foundation
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS faculty.sites.uci.edu. cell, also called the electrochemical force (emf). This is primarily expressed as Gibbs free energy of the charge of the cell, ∆G cell As reaction occurs, there is a decrease in the free energy of the cell according to: ∆G cell = ‐nFE cell where E cell,is related to the sum of the standard potential of https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrochemical_potential Oxidation-reduction or redox reactions take place in electrochemical cells. There are two types of electrochemical cells. Spontaneous reactions occur in galvanic (voltaic) cells; nonspontaneous reactions occur in electrolytic cells. Both types of cells contain electrodes where the oxidation and.
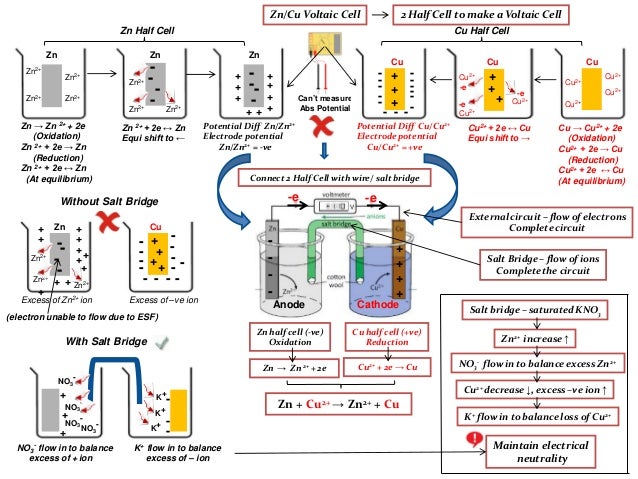
Introduction of Electrochemical Concepts (PDF 26P) This note covers the following topics: Electrochemical Cells, Electrochemical Potentials, Reference Electrodes, Electrochemical Cells and Reactions, Electrified Interfaces, Electrochemical Experiment and Variables in Electrochemical Cells, Mass Transport, Current-Voltage Curve Shapes. 2 1 Introduction to Electrochemical Cells designs in order to prevent short - circuit by battery reverse installation, and they are shaped so as to match the receptacle facilities provided in the appliances.
Cells and batteries: page 8 of 21 Cell performance You will have seen that the voltage of an electrochemical cell decreases as the chemicals get used up. In this next part you will investigate factors that might influence the potential difference of an electrochemical cell. The cell you will use consists of the two half cells: Mg(s)/Mg2+(aq) and Cu(s)/Cu2+(aq) Make an electrochemical cell cell, also called the electrochemical force (emf). This is primarily expressed as Gibbs free energy of the charge of the cell, ∆G cell As reaction occurs, there is a decrease in the free energy of the cell according to: ∆G cell = ‐nFE cell where E cell,is related to the sum of the standard potential of
An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that drives a non-spontaneous redox reaction through the application of electrical energy. They are often used to decompose chemical compounds, in a process called electrolysis—the Greek word lysis means to break up. The micro fuel cell-type electrochemical sensors do not require an external driving voltage. For example, an elec-trochemical sensor specific to oxygen has an anode, ei-ther Pb or Cd, that supplies electrons for the reduction of oxygen at the cathode. During the oxidation of the an-ode, the electrons are released which then travel via an external circuit to the cathode where oxygen molecules
Lecture 2: Basic Physics of Galvanic Cells & Electrochemical Energy Conversion In this lecture, we talk about the basic science of the galvanic cells and give several commonly-seen examples in real application. 1: Electrochemical cells and its operating parts The galvanic cell, or called voltaic cell, is an electrochemical cell that converts ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a series of electrochemical cells. For each cell, you will measure the voltage and compare it with the calculated standard value. You will learn about the accuracy of electrochemical measurements
This author argues that conventions make electrochemistry harder for students to learn and much harder to remember. For this reason, instructors must connect our presentation of galvanic cells more closely with the physical world of galvanic cells than "conventional" electrochemistry does. In its turn, the electrochemical cell is divided by two groups: voltaic or galvanic cells and electrolytic cells. Galvanic cells convert a chemical energy to an electrical energy and electrolytic cells do a conversion oppositely. In this practical, there were used the galvanic cells. [1] Galvanic cell consists of two half-cells, external
Electrochemistry is the study of reactions in which charged particles (ions or electrons) cross the interface between two phases of matter, typically a metallic phase (the electrode) and a conductive solution, or electrolyte. A process of this kind is known generally as an electrode process. Electrode processes (reactions) take place at the surface of the electrode, and produce a slight Electrochemical Cells Under Nonstandard Conditions. If we can use cell potential to determine free energies then it follows that we can use free energies to determine cell potential. e.g. We wish to know whether the reaction described by the cell below is spontaneous and, if so, what is its potential. We can look up the standard reduction potential for a Cl2/Cl- half-cell, but there is no
Electrochemical Cells Electrochemistry involves redox reactions. Terminology: Red-ox reaction – a chemical reaction where one species undergoes a loss of electrons another species gains 13.4 Processes in electrochemical cells (ESCR7) Half-cells and half-reactions (ESCR8) Galvanic cells are actually made up of two half-cells. One half-cell contains the anode and an electrolyte containing the same metal cations.
Electrochemistry is the study of reactions in which charged particles (ions or electrons) cross the interface between two phases of matter, typically a metallic phase (the electrode) and a conductive solution, or electrolyte. A process of this kind is known generally as an electrode process. Electrode processes (reactions) take place at the surface of the electrode, and produce a slight ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a series of electrochemical cells. For each cell, you will measure the voltage and compare it with the calculated standard value. You will learn about the accuracy of electrochemical measurements
Electrochemical Cells Revised: 5/04/05 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one chemical species to another. The energy from a redox reaction can be used to accomplish work by constructing an electrochemical cell. In an electrochemical cell, the oxidation process and the reduction Before developing analytical methods based on electrochemistry, it is worth exploring aspects about electrochemical cells. Concepts needed to comprehend the nature of an electrochemical cell are informative in understanding some of the analytical methods we will develop.
Electrochemical Cells Revised: 5/04/05 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one chemical species to another. The energy from a redox reaction can be used to accomplish work by constructing an electrochemical cell. In an electrochemical cell, the oxidation process and the reduction half-cell reactions; together they are also called, for obvious reasons, redox reactions. In an electrochemical cell, a minimum of two half cell reactions must occur,one at the cathode and one at the anode. Electrolyte in anode and cathode chamber in cells with diaphragms/separators is called anolyte and catholyte respectively.
Electrochemical Cells Worksheet 1. Calculate the standard cell potential produced by a galvanic cell consisting of a nickel electrode in contact with a solution of Ni2+ +ions and a silver electrode in contact with a solution of Ag ions. Which is anode and which is the cathode? 2. What is the voltage produced by a galvanic ell consisting of an Electrochemistry is the study of reactions in which charged particles (ions or electrons) cross the interface between two phases of matter, typically a metallic phase (the electrode) and a conductive solution, or electrolyte. A process of this kind is known generally as an electrode process. Electrode processes (reactions) take place at the surface of the electrode, and produce a slight