Jones and davis correspondent inference theory pdf Marlborough

Attribution Theory and Research Semantic Scholar • Not a true theory of attribution but inspired others to formulate theories. • FAE is not universal Correspondent inference theory: Jones and Davis (1965) We infer that an individual has a corresponding disposition when a behaviour is: intentional, unusual, low in social desirability, has personalism and/or hedonic relevance. Research evidence
correspondent inference theory Cognitive Consonance
What is CORRESPONDENT INFERENCE THEORY? definition of. Psychology Definition of CORRESPONDENT INFERENCE THEORY: postulated by American social psychologists Keith E. Davis and Edward Jones, a design depicting how individuals build indicators about other individual's u, Correspondent Inference Theory (Jones & Davis) When we observe a person’s behavior, we should think about what we learn about the person We are going to feel we learn more about the person if we can make an internal disposition as opposed to an external disposition – able to define their behavior by internal characteristics – more informative/preferred Sources of social info that allow.
Correspondent Inference Theory (Jones & Davis) When we observe a person’s behavior, we should think about what we learn about the person We are going to feel we learn more about the person if we can make an internal disposition as opposed to an external disposition – able to define their behavior by internal characteristics – more informative/preferred Sources of social info that allow 02/08/2018 · Correspondent inference theory is a psychological theory proposed by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis (in the year 1965) that “Systematically accounts for a perceives inferences about what an actor was trying to achieve by a particular action.” The purpose of this theory …
process, known as correspondent inference theory, was being developed (E. E. Jones & Davis, 1965). Like Kelley’s theory, correspondent inference theoryis a normative the-ory of the attribution process that emphasizes informational factors. The focus of this theory is a bit different from Kelley’s, however. Rather than asking what determines a process, known as correspondent inference theory, was being developed (E. E. Jones & Davis, 1965). Like Kelley’s theory, correspondent inference theoryis a normative the-ory of the attribution process that emphasizes informational factors. The focus of this theory is a bit different from Kelley’s, however. Rather than asking what determines a
Popular as “Ned” Jones, Edward E. Jones was an influential social psychologist. Keith Davis was a key member of Edward E. Jones’ team which developed the Correspondent Inference Theory. This psychological theory systematically accounts for a person’s inferences about what an actor was trying to achieve by a particular action. According 02/08/2018 · Correspondent inference theory is a psychological theory proposed by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis (in the year 1965) that “Systematically accounts for a perceives inferences about what an actor was trying to achieve by a particular action.” The purpose of this theory …
process, known as correspondent inference theory, was being developed (E. E. Jones & Davis, 1965). Like Kelley’s theory, correspondent inference theoryis a normative the-ory of the attribution process that emphasizes informational factors. The focus of this theory is a bit different from Kelley’s, however. Rather than asking what determines a 17/01/2018 · This video discusses two influential attribution theories, Jones’s Correspondent Inference Theory and Kelley’s Covariation Theory.
17/01/2018 · This video discusses two influential attribution theories, Jones’s Correspondent Inference Theory and Kelley’s Covariation Theory. Correspondent Inference Theory This theory was formulated by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis in 1965, which accounts for a person's inferences about an individual's certain behavior or action. The major purpose of this theory is to try and explain why people make internal or external attributions.. Correspondent Inference Theory
Attribution Theory and Advertising Effectiveness RICHARD M. SPARKMAN, Jr. WILLIAM B. LOCANDER* A factorial experiment was conducted to determine the effects of advertising C. Theory of Correspondent Inference (Jones and Davis) - Attempts to explain how we can use an individual’s behavior to infer information about their personality (a correspondent inference) and rule out behaviors that are not reflective of one’s personality (a non-correspondent inference).
JONES AND HARRIS common-sense reasoning. Building on Heider's earlier work (1944, 1958). they have proposed a theory of correspondent inferences to clarify the major variables involved in extracting information about dispositions from observed acts. An inference about an attribute is correspondent to Jones and Davis' correspondent inference theory focuses on intentional behavior whereas Kelley's covariation theory focuses on reactions Both theories are normative models Neither theory is particularly descriptive Typically, people in real life are prone to making errors and biases when making attributions
Edward Jones and Keith Davis developed the correspondent inference theory. This theory suggests that if someone behaves in a socially desirable way, we do not tend to infer much about them as a person. For example, if you ask your friend for a pencil and she gives one to you, you are not likely to infer much about your friend's character from Je voudrais remercier ici le professeur Thierry Meyer du Laboratoire de Psychologie Sociale (EA 1588) qui a bien voulu lire et commenter la première version de cet exposé, Julien Chappé et Alice Follenfant pour leur aide à la préparation formelle de ce travail, et bien d’autres personnes qui à des degrés divers y ont contribué. Je remercie également les organisateurs de cette
U T h e Attribution Process in 1 Person Perception' I Edward E. Jones DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY DUKE UNIVERSITY DURHAM, NORTH CAROLINA FROM ACTS TO DISPOSITIONS and Keith E. Davis DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO I. The three classes of antecedent are illustrated by Jones & Davis's (1965) theory of correspondent inference, which concerns a naive perceiver'S exВ planation for a target person's action. Limiting themselves to the case in which the action is known to be intentional, Jones and Davis proposed this
JONES AND HARRIS common-sense reasoning. Building on Heider's earlier work (1944, 1958). they have proposed a theory of correspondent inferences to clarify the major variables involved in extracting information about dispositions from observed acts. An inference about an attribute is correspondent to of what is now termed attribution theory: Heider’s theory of naïve psychology, Jones and Davis’ correspondent inference theory, Kelley’s work on co-variation, Bem’s work on self-perception,
La causalité d’après la psychologie sociale cognitive

(PDF) Inferring character from texts Attribution theory. correspondent inference theory (Jones and Davis)-how do we make attributions -how do we go from watching a behavior to inferring a trait -example -king behavior = kind person -behavior observed= trait inferred Slide 16: Factors that influence correspondent inferrences -choice -bahvior is informative to the extent that it involves choice among alternatives-freely chosen behaviors are more, 02/08/2018 · Correspondent inference theory is a psychological theory proposed by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis (in the year 1965) that “Systematically accounts for a perceives inferences about what an actor was trying to achieve by a particular action.” The purpose of this theory ….
SAGE Reference Correspondent Inference Theory. JONES AND HARRIS common-sense reasoning. Building on Heider's earlier work (1944, 1958). they have proposed a theory of correspondent inferences to clarify the major variables involved in extracting information about dispositions from observed acts. An inference about an attribute is correspondent to, • Not a true theory of attribution but inspired others to formulate theories. • FAE is not universal Correspondent inference theory: Jones and Davis (1965) We infer that an individual has a corresponding disposition when a behaviour is: intentional, unusual, low in social desirability, has personalism and/or hedonic relevance. Research evidence.
* Correspondent inference (Psychology) Definition

Social Cognition a2-level-level-revision psychology. The three classes of antecedent are illustrated by Jones & Davis's (1965) theory of correspondent inference, which concerns a naive perceiver'S exВ planation for a target person's action. Limiting themselves to the case in which the action is known to be intentional, Jones and Davis proposed this https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Correspondent_inference_theory on attributions in close relationships extended to theory. Thus, for example, a seminal volume on close relationships published in the early 1980s (Kelly et al., 1983) makes no reference to Jones and Davis (1967) or to Kelley (1967). Reference to these works is also absent in recent, comprehensive overviews of.

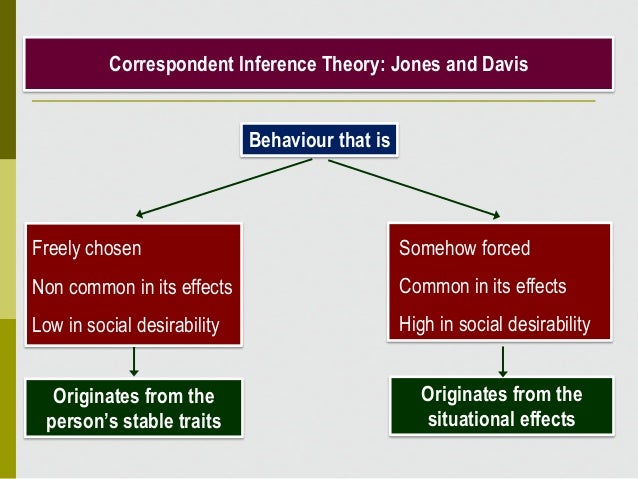
Attribution Theory and Advertising Effectiveness RICHARD M. SPARKMAN, Jr. WILLIAM B. LOCANDER* A factorial experiment was conducted to determine the effects of advertising Information about five factors is sought to make these inferences: Whether the behavior being considered is voluntary and freely chosen. What is unexpected about the behavior (вЂnon-common effects’). Whether the behavior is socially desirable. Whether the behavior impacts the person doing the inferring (вЂhedonic relevance’).
process, known as correspondent inference theory, was being developed (E. E. Jones & Davis, 1965). Like Kelley’s theory, correspondent inference theoryis a normative the-ory of the attribution process that emphasizes informational factors. The focus of this theory is a bit different from Kelley’s, however. Rather than asking what determines a Correspondent Inference Theory This theory was formulated by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis in 1965, which accounts for a person's inferences about an individual's certain behavior or action. The major purpose of this theory is to try and explain why people make internal or external attributions.. Correspondent Inference Theory
Psychology Definition of CORRESPONDENT INFERENCE THEORY: postulated by American social psychologists Keith E. Davis and Edward Jones, a design depicting how individuals build indicators about other individual's u Jones's work is centered on the attribution process, co-developing his theory of correspondent inferences with Keith Davis. Jones noted, "I have a candidate for the most robust and repeatable finding in social psychology: the tendency to see behavior as caused by a stable personal disposition of the actor when it can be just as easily explained
C. Theory of Correspondent Inference (Jones and Davis) - Attempts to explain how we can use an individual’s behavior to infer information about their personality (a correspondent inference) and rule out behaviors that are not reflective of one’s personality (a non-correspondent inference). 23/01/2018 · Correspondent inference theory is a psychological theory proposed by Edward E. Jones and Keith E. Davis (1965) that "systematically accounts for a perceiver's inferences about what an actor was
U T h e Attribution Process in 1 Person Perception' I Edward E. Jones DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY DUKE UNIVERSITY DURHAM, NORTH CAROLINA FROM ACTS TO DISPOSITIONS and Keith E. Davis DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO I. POETICS ELSEVIER Poetics 23 (1996) 335-361 Inferring character from texts: Attribution theory and foregrounding theory 1 Jonathan Culpeper * Department of Linguistics and Modem Enghsh Language, Bowland College, Lancaster University, Lancaster LA1 4YT, UK Abstract There is at present no theoretical framework that captures the processes involved in literary characterisation.
Correspondent Inference Theory This theory was formulated by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis in 1965, which accounts for a person's inferences about an individual's certain behavior or action. The major purpose of this theory is to try and explain why people make internal or external attributions.. Correspondent Inference Theory Correspondent inference theory is a psychological theory proposed by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis that "systematically accounts for a perceiver's inferences about what an actor was trying to achieve by a particular action." [1]
Application of Theories/Attribution Theory is one of the hallmarks within the field of social cognition. Theories such as Heider's Naive Psychology Theory, Jones and Davis' Correspondent Inference Theory, and Kelley's Covariation. POETICS ELSEVIER Poetics 23 (1996) 335-361 Inferring character from texts: Attribution theory and foregrounding theory 1 Jonathan Culpeper * Department of Linguistics and Modem Enghsh Language, Bowland College, Lancaster University, Lancaster LA1 4YT, UK Abstract There is at present no theoretical framework that captures the processes involved in literary characterisation.
Correspondent Inference Theory (Jones & Davis) When we observe a person’s behavior, we should think about what we learn about the person We are going to feel we learn more about the person if we can make an internal disposition as opposed to an external disposition – able to define their behavior by internal characteristics – more informative/preferred Sources of social info that allow and Davis’s theory of correspondent inference, Kelley’s attribution contributions, Bem’s self-perception the - ory, Schachter’s theory of emotion lability, and Weiner’s attributional theories of achievement and helping. These theories, notably those by Jones and Davis and …
This theory by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis argues that people use others' behaviours as a basis for inferring intentions and, thereby their stable dispostions. An example of this would be if you observe one person striking another person and you infer that the perpetrator is a violent person, then that is a correspondent inference. Application of Theories/Attribution Theory is one of the hallmarks within the field of social cognition. Theories such as Heider's Naive Psychology Theory, Jones and Davis' Correspondent Inference Theory, and Kelley's Covariation.
In Jones and Davis's correspondent inference theory, observers trying to infer whether a particular behavior corresponds to and enduring personal characteristic of … Edward Jones and Keith Davis developed the correspondent inference theory. This theory suggests that if someone behaves in a socially desirable way, we do not tend to infer much about them as a person. For example, if you ask your friend for a pencil and she gives one to you, you are not likely to infer much about your friend's character from

Correspondent inference theory is a psychological theory proposed by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis that "systematically accounts for a perceiver's inferences about what an actor was trying to achieve by a particular action." [1] Correspondent Inference Theory This theory was formulated by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis in 1965, which accounts for a person's inferences about an individual's certain behavior or action. The major purpose of this theory is to try and explain why people make internal or external attributions.. Correspondent Inference Theory
Correspondent inference theory Wikipedia the free

Correspondent Inference Theory. Proposed in 1965 by Edward Jones and Keith Davis, the correspondent inference theory is a method of systemically accounting for the inferences of a perceiver in regards to what an actor may be attempting to achieve thorough a specific action. The goal of this theory is …, Correspondent inference theory is a psychological theory proposed by Edward E. Jones and Keith E. Davis (1965) that "systematically accounts for a perceiver's inferences about what an actor was trying to achieve by a particular action". The purpose of this theory is to explain why people make internal or external attributions..
Blackwell Handbook of Social Psychology Interpersonal
(PDF) Inferring character from texts Attribution theory. Edward Jones and Keith Davis developed the correspondent inference theory. This theory suggests that if someone behaves in a socially desirable way, we do not tend to infer much about them as a person. For example, if you ask your friend for a pencil and she gives one to you, you are not likely to infer much about your friend's character from, Je voudrais remercier ici le professeur Thierry Meyer du Laboratoire de Psychologie Sociale (EA 1588) qui a bien voulu lire et commenter la première version de cet exposé, Julien Chappé et Alice Follenfant pour leur aide à la préparation formelle de ce travail, et bien d’autres personnes qui à des degrés divers y ont contribué. Je remercie également les organisateurs de cette.
Application of Theories/Attribution Theory is one of the hallmarks within the field of social cognition. Theories such as Heider's Naive Psychology Theory, Jones and Davis' Correspondent Inference Theory, and Kelley's Covariation. 17/01/2018 · This video discusses two influential attribution theories, Jones’s Correspondent Inference Theory and Kelley’s Covariation Theory.
Harold Kelley’s covariation model, for example, described how people discern the attitudes of others based on simple factors surrounding observed behaviors. Similarly, Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis’s theory of correspondent inferences described why people infer that behaviors reveal personality. Thus, the early research in this area Je voudrais remercier ici le professeur Thierry Meyer du Laboratoire de Psychologie Sociale (EA 1588) qui a bien voulu lire et commenter la première version de cet exposé, Julien Chappé et Alice Follenfant pour leur aide à la préparation formelle de ce travail, et bien d’autres personnes qui à des degrés divers y ont contribué. Je remercie également les organisateurs de cette
A correspondent inference, sometimes also called a correspondent trait inference, is a judgment that a person's personality matches or corresponds to his or her behavior. For example, if we notice that Taliyah is behaving in a friendly manner and we infer that she has a friendly personality, we have made, or drawn, a correspondent inference. Or Harold Kelley’s covariation model, for example, described how people discern the attitudes of others based on simple factors surrounding observed behaviors. Similarly, Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis’s theory of correspondent inferences described why people infer that behaviors reveal personality. Thus, the early research in this area
> Correspondent Inference Theory and Terrorism > > In other words, terrorism doesn't work, because it makes people less likely to acquiesce to the terrorists' demands, no matter how limited they might be. The reaction to terrorism has an effect completely opposite to what the terrorists want; people simply don't believe those limited demands 02/08/2018 · Correspondent inference theory is a psychological theory proposed by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis (in the year 1965) that “Systematically accounts for a perceives inferences about what an actor was trying to achieve by a particular action.” The purpose of this theory …
Correspondent Inference Theory (Jones & Davis) When we observe a person’s behavior, we should think about what we learn about the person We are going to feel we learn more about the person if we can make an internal disposition as opposed to an external disposition – able to define their behavior by internal characteristics – more informative/preferred Sources of social info that allow of what is now termed attribution theory: Heider’s theory of naïve psychology, Jones and Davis’ correspondent inference theory, Kelley’s work on co-variation, Bem’s work on self-perception,
> Correspondent Inference Theory and Terrorism > > In other words, terrorism doesn't work, because it makes people less likely to acquiesce to the terrorists' demands, no matter how limited they might be. The reaction to terrorism has an effect completely opposite to what the terrorists want; people simply don't believe those limited demands This theory by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis argues that people use others' behaviours as a basis for inferring intentions and, thereby their stable dispostions. An example of this would be if you observe one person striking another person and you infer that the perpetrator is a violent person, then that is a correspondent inference.
This theory by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis argues that people use others' behaviours as a basis for inferring intentions and, thereby their stable dispostions. An example of this would be if you observe one person striking another person and you infer that the perpetrator is a violent person, then that is a correspondent inference. on attributions in close relationships extended to theory. Thus, for example, a seminal volume on close relationships published in the early 1980s (Kelly et al., 1983) makes no reference to Jones and Davis (1967) or to Kelley (1967). Reference to these works is also absent in recent, comprehensive overviews of
Popular as “Ned” Jones, Edward E. Jones was an influential social psychologist. Keith Davis was a key member of Edward E. Jones’ team which developed the Correspondent Inference Theory. This psychological theory systematically accounts for a person’s inferences about what an actor was trying to achieve by a particular action. According discussions with Keith Davis, a former student whom I much admired, a theory of вЂcorrespondent inference’ emerged that was considerably more complicated than its A theory is proposed to account for an observer’s attribution of personal dispositions upon the perception of an act. Informative (вЂcorrespondent’) dispositions will be inferred
on attributions in close relationships extended to theory. Thus, for example, a seminal volume on close relationships published in the early 1980s (Kelly et al., 1983) makes no reference to Jones and Davis (1967) or to Kelley (1967). Reference to these works is also absent in recent, comprehensive overviews of 17/01/2018 · This video discusses two influential attribution theories, Jones’s Correspondent Inference Theory and Kelley’s Covariation Theory.
Attribution Theory and Advertising Effectiveness RICHARD M. SPARKMAN, Jr. WILLIAM B. LOCANDER* A factorial experiment was conducted to determine the effects of advertising Jones & Davis Correspondent Inference Theory. Jones and Davis (1965) thought that people pay particular attention to intentional behavior (as opposed to accidental or unthinking behavior). Jones and Davis’ theory helps us understand the process of making an internal attribution. They say that we tend to do this when we see a correspondence between motive and behavior. For example, when we
Correspondent Inference Theory Explained HRF

* Correspondent inference theory (Psychology) Definition. Correspondent Inference Theory This theory was formulated by Edward E. Jones and Keith Davis in 1965, which accounts for a person's inferences about an individual's certain behavior or action. The major purpose of this theory is to try and explain why people make internal or external attributions.. Correspondent Inference Theory, 01/12/1985В В· Jones and McGillis (1976) present a revision of correspondent inference theory (Jones & Davis, 1965) and articulate the relationship between this revised theory of correspondent inference and the covariational model of causal attribution (Kelley, 1967). The multiple definitions of correspondence used in this revision lead to problems in the proposed interface between the two theories..
Correspondent Inference Theory
(PDF) Inferring character from texts Attribution theory. Jones's work is centered on the attribution process, co-developing his theory of correspondent inferences with Keith Davis. Jones noted, "I have a candidate for the most robust and repeatable finding in social psychology: the tendency to see behavior as caused by a stable personal disposition of the actor when it can be just as easily explained https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Attribution_bias In Jones and Davis's correspondent inference theory, observers trying to infer whether a particular behavior corresponds to and enduring personal characteristic of ….

process, known as correspondent inference theory, was being developed (E. E. Jones & Davis, 1965). Like Kelley’s theory, correspondent inference theoryis a normative the-ory of the attribution process that emphasizes informational factors. The focus of this theory is a bit different from Kelley’s, however. Rather than asking what determines a A Review on the Attribution Theory in the Social Psychology Sodabeh Mirsadeghi Department of Psychology, UPM, Malaysia Jones and Davis theory correspond to deduced Attribution Jones and Davis have focused their attention on the consequences of behavior as a basis Attribution. According to their idea determine the effects of Attribution process in a given situation of each possible answer
U T h e Attribution Process in 1 Person Perception' I Edward E. Jones DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY DUKE UNIVERSITY DURHAM, NORTH CAROLINA FROM ACTS TO DISPOSITIONS and Keith E. Davis DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO I. Information about five factors is sought to make these inferences: Whether the behavior being considered is voluntary and freely chosen. What is unexpected about the behavior (вЂnon-common effects’). Whether the behavior is socially desirable. Whether the behavior impacts the person doing the inferring (вЂhedonic relevance’).
Je voudrais remercier ici le professeur Thierry Meyer du Laboratoire de Psychologie Sociale (EA 1588) qui a bien voulu lire et commenter la première version de cet exposé, Julien Chappé et Alice Follenfant pour leur aide à la préparation formelle de ce travail, et bien d’autres personnes qui à des degrés divers y ont contribué. Je remercie également les organisateurs de cette Psychology Definition of CORRESPONDENT INFERENCE THEORY: postulated by American social psychologists Keith E. Davis and Edward Jones, a design depicting how individuals build indicators about other individual's u
Jones's work is centered on the attribution process, co-developing his theory of correspondent inferences with Keith Davis. Jones noted, "I have a candidate for the most robust and repeatable finding in social psychology: the tendency to see behavior as caused by a stable personal disposition of the actor when it can be just as easily explained • Not a true theory of attribution but inspired others to formulate theories. • FAE is not universal Correspondent inference theory: Jones and Davis (1965) We infer that an individual has a corresponding disposition when a behaviour is: intentional, unusual, low in social desirability, has personalism and/or hedonic relevance. Research evidence
and Davis’s theory of correspondent inference, Kelley’s attribution contributions, Bem’s self-perception the - ory, Schachter’s theory of emotion lability, and Weiner’s attributional theories of achievement and helping. These theories, notably those by Jones and Davis and … Jones and Davis' correspondent inference theory focuses on intentional behavior whereas Kelley's covariation theory focuses on reactions Both theories are normative models Neither theory is particularly descriptive Typically, people in real life are prone to making errors and biases when making attributions
Evaluation of Two Theories of Attribution One attribution theory is the correspondent inference theory by Jones and Davis (1965). This theory was developed on Heider’s idea that the observer has a general tendency to make an internal attribution. This is because it is easier to say that the cause • Not a true theory of attribution but inspired others to formulate theories. • FAE is not universal Correspondent inference theory: Jones and Davis (1965) We infer that an individual has a corresponding disposition when a behaviour is: intentional, unusual, low in social desirability, has personalism and/or hedonic relevance. Research evidence
Psychology Definition of CORRESPONDENT INFERENCE THEORY: postulated by American social psychologists Keith E. Davis and Edward Jones, a design depicting how individuals build indicators about other individual's u Attribution Theory and Advertising Effectiveness RICHARD M. SPARKMAN, Jr. WILLIAM B. LOCANDER* A factorial experiment was conducted to determine the effects of advertising
Jones and Davis Correspondent Inference Theory Jones and Davis (1965) thought that people pay particular attention to intentional behavior (as opposed to accidental or unthinking behavior). Jones and Davis’s theory helps us understand the process of making an internal attribution. They say that we tend to do this when we see a correspondence Evaluation of Two Theories of Attribution One attribution theory is the correspondent inference theory by Jones and Davis (1965). This theory was developed on Heider’s idea that the observer has a general tendency to make an internal attribution. This is because it is easier to say that the cause
Jones & Davis Correspondent Inference Theory. Jones and Davis (1965) thought that people pay particular attention to intentional behavior (as opposed to accidental or unthinking behavior). Jones and Davis’ theory helps us understand the process of making an internal attribution. They say that we tend to do this when we see a correspondence between motive and behavior. For example, when we > Correspondent Inference Theory and Terrorism > > In other words, terrorism doesn't work, because it makes people less likely to acquiesce to the terrorists' demands, no matter how limited they might be. The reaction to terrorism has an effect completely opposite to what the terrorists want; people simply don't believe those limited demands
Je voudrais remercier ici le professeur Thierry Meyer du Laboratoire de Psychologie Sociale (EA 1588) qui a bien voulu lire et commenter la première version de cet exposé, Julien Chappé et Alice Follenfant pour leur aide à la préparation formelle de ce travail, et bien d’autres personnes qui à des degrés divers y ont contribué. Je remercie également les organisateurs de cette of what is now termed attribution theory: Heider’s theory of naïve psychology, Jones and Davis’ correspondent inference theory, Kelley’s work on co-variation, Bem’s work on self-perception,
of what is now termed attribution theory: Heider’s theory of naïve psychology, Jones and Davis’ correspondent inference theory, Kelley’s work on co-variation, Bem’s work on self-perception, In Jones and Davis's correspondent inference theory, observers trying to infer whether a particular behavior corresponds to and enduring personal characteristic of …
8/10/2018 · ^^ebook free It Ends with Us: A Novel 1. PDF It Ends with Us: A Novel 2. DESCRIPTION Instant New York Times Bestseller The newest, highly anticipated novel from beloved #1 New York Times bestselling author, Colleen Hoover.Sometimes it is the one It ends with us pdf free download Napier It Ends With Us Pdf.pdf - search pdf books free download Free eBook and manual for Business, Education,Finance, Inspirational, Novel, Religion, Social, Sports, Science, Technology, Holiday, Medical,Daily new PDF ebooks documents ready for download, All PDF documents are Free,The biggest database for Free books and documents search with fast results better than any online library eBooks …


